1,686 total views, 4 views today
E-mail inbox suppliers such as Gmail utilize your IP reputation, also known as IP score, or e-mail sender reputation to decide whether your email has to send to the inbox or not. You want to be sure that your emails do not reach the SPAM folders of your contacts.
Email providers utilize various systems to monitor activity and evaluate the potential danger to each IP address that provides messages to their network. There are some points to consider in order to monitor and keep a good Sender Reputation.
Read Also about: How to Check Your Sending Reputation
1. Look at Key Metrics:
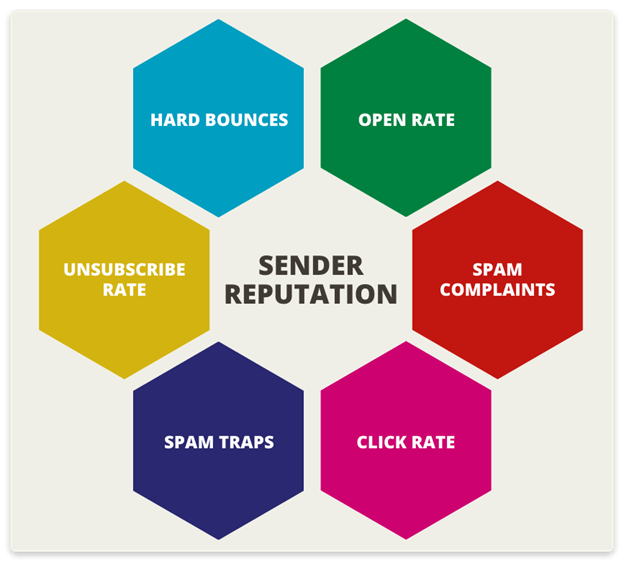
Four major metrics mentioned below should be kept in mind by email senders when they check their reputation as senders:
Acceptance rate – Greater or equal to 98% means good Sender Reputation and a high acceptance rate for delivery and below 94% means bad reputation.
Bounce rate – Less than 2% bounce rate is good for avoiding rejection and greater than 9% is bad.
Open rate – If the open rate is 18% or high then it is good and for less than 6% open rate is bad.
Spam rate – The percentage of spam rate (emails reported as spam) should be less than 0.02%. Greater than 0.05% is bad.
2. By domains break down the data:
One helpful thing to know is whether the IP or domain reputation problem occurs in all domains or is confined to one or more domains. Break your key metrics into the top 10 or 20 domains you send emails to and examine the section. Note changes in open rate, bounce rate, spam rate, acceptation rate, or whatever you choose to concentrate on.
We suggest that you plan such an analysis for a time. The more frequent you send, the more regularly you’ll want to evaluate the data, for example, every 30 days, 60 days, or 90 days. It will help you analyze seasonal fluctuations, and general patterns, and uncover the deliverability difficulties with individual mailboxes.
3. Separate Mail Streams by Domains:
You carry a domain reputation across all email service providers like your credit history. You may send commercial and transactional emails with the help of an email service provider and send internal company emails via Gmail or Office 365. And, if marketing emails impact the placing of your internal and transactional emails, this impact is customized because the domain is the same.
We suggest that for different sorts of email, for example internal, transactional, and marketing emails, use distinct subdomains (for example, marketing.domain.com, news.domain.com, support.domain.com…) to keep your primary domain safe.
4. Be aware of the setup and use of your domain:
When setting up a new domain, make sure all your authentication records are configured and the volume from the new domain/subdomain of e-mails progressively increases. You have a domain created and you should keep a watch on how it is utilized over the internet. Add a DMARC record to your DNS and get DMARC reports.
5. Use Monitoring Tools:
The right tools will help you to monitor your domain. You have the tools at your disposal at GlockApps. “Inbox email tester” enables you to monitor and detect when your message starts going to spam with different mailbox providers. With DMARC Analytics, you will get an idea of who sends e-mails on behalf of your domain and how messages are validated from each source.
Read Also about 5 tools to check your sending reputation